Lewis Dot Structure Bond Calculator
A bond is the sharing of 2 electrons. Covalent bonds share electrons in order to form a stable octet around each atom in the molecules. Hydrogen is the exception it only requires 2 electrons (a duet) to be stable. How do we draw a covalent Lewis Dot Structure? Level 1 (basic) 1. Add up all the valance electrons of the atoms involved. ex CF4 So C has 4 and F has 7 (x4 we have 4Fs) = 32 valence electrons 2. You need to pick the central atom. This is usually easy, this atom will be surrounded by the others. Never H. So C will be surrounded by F's. 3. Now we create our skeleton structure by placing bonds in. A bond is a dash that represents 2 electrons. We have now placed 8 electrons as 4 bonds. We have 32-8= 24 more to place. 4. Starting with the outer atoms add the remaining electrons in pairs until all the electrons have run out.
All 32 electrons are now in place, count the dots around each F. 6 dots and a bond (2 electrons) is 8. We have our octet. The carbon has 4 bonds (2electrons) for its 8. DONE Level 2 (Double and Triple bonds) Same rules apply until #4 1. Add up all the valance electrons of the atoms involved. ex CO2 So C has 4 and O has 6 (x2 ) = 16 valence electrons 2. You need to pick the central atom. This is usually easy, this atom will be surrounded by the others. Never H. So C will be surrounded by O's. 3. Now we create our skeleton structure by placing bonds in. A bond is a dash that represents 2 electrons. We have now placed 4 electrons as 2 bonds. We have 16-4=12 more to place. 4. Starting with the outer atoms add the remaining electrons in pairs until all the electrons have run out.
All 16 electrons are now in place, count the dots around each O. 6 dots and a bond (2 electrons) is 8. We have our octet. The carbon has 2 bonds (2electrons) for its 4....? We need 8, so move a pair of electrons from the O to between the C and O. It will share 2 pairs of electrons instead of 1. It now has a double bond instead of a single bond.
now they all have an octet, it cleans up like this Make it symmetrical. Level 3-Lewis Dots of Polyatomic Ions Same rules apply, at the end they get brackets and a charge AP Chemistry and or College Level Rules 1. Determine whether the compound is covalent or ionic. If covalent, treat the entire molecule. If ionic, treat each ion separately. Compounds of low electronegativity metals with high electronegativity nonmetals (DEN > 1.7) are ionic as are compounds of metals with polyatomic anions. For a monoatomic ion, the electronic configuration of the ion represents the correct Lewis structure. For compounds containing complex ions, you must learn to recognize the formulas of cations and anions. 2. Determine the total number of valence electrons available to the molecule or ion by:
3. Organize the atoms so there is a central atom (usually the least electronegative) surrounded by ligand (outer) atoms. Hydrogen is never the central atom. 4. Determine a provisional electron distribution by arranging the electron pairs (E.P.) in the following manner until all available pairs have been distributed:
5. Calculate the formal charge (F) on the central atom.
6. If the central atom formal charge is zero or is equal to the charge on the species, the provisional electron distribution from (4) is correct. Calculate the formal charge of the ligand atoms to complete the Lewis structure. 7. If the structure is not correct, calculate the formal charge on each of the ligand atoms. Then to obtain the correct structure, form a multiple bond by sharing an electron pair from the ligand atom that has the most negative formal charge.
8. Recalculate the formal charge of each atom to complete the Lewis structure. on to Formal Charge Chemical Demonstration Videos |
Get the free 'Lewis structure' widget for your website, blog, Wordpress, Blogger, or iGoogle. Find more Chemistry widgets in Wolfram Alpha.
This demo will convert a skeletal figure, provided by a drawing in the HTML5 SketcherCanvas component on the left, into a Lewis Dot Structure in the Canvas on the right. When you are finished drawing your 2D structure, click on the Get Lewis Dot Structure button to see the result. Lewis dot structures (or just Lewis structures) were developed around 1920 by pioneering chemist Gilbert Lewis, as a way of picturing chemical bonding in molecules. We draw Lewis structures to. Discover the bonding arrangement of atoms,; Discover whether there is any degeneracy of bonding (more on that later),; Figure out whether a given group of atoms might even bond together to form a.
Lewis Structures are important to learn because they help us predict:
- the shape of a molecule.
- how the molecule might react with other molecules.
- the physical properties of the molecule (like boiling point, surface tension, etc.).
That helps us understand and predict interactions with things like medicine and our body, materials used to make buildings and airplanes, and all sorts of other substances. Lewis structures don't tell us everything, but along with molecule geometry and polarity they are hugely informative.
Lewis Dot Structure Calc
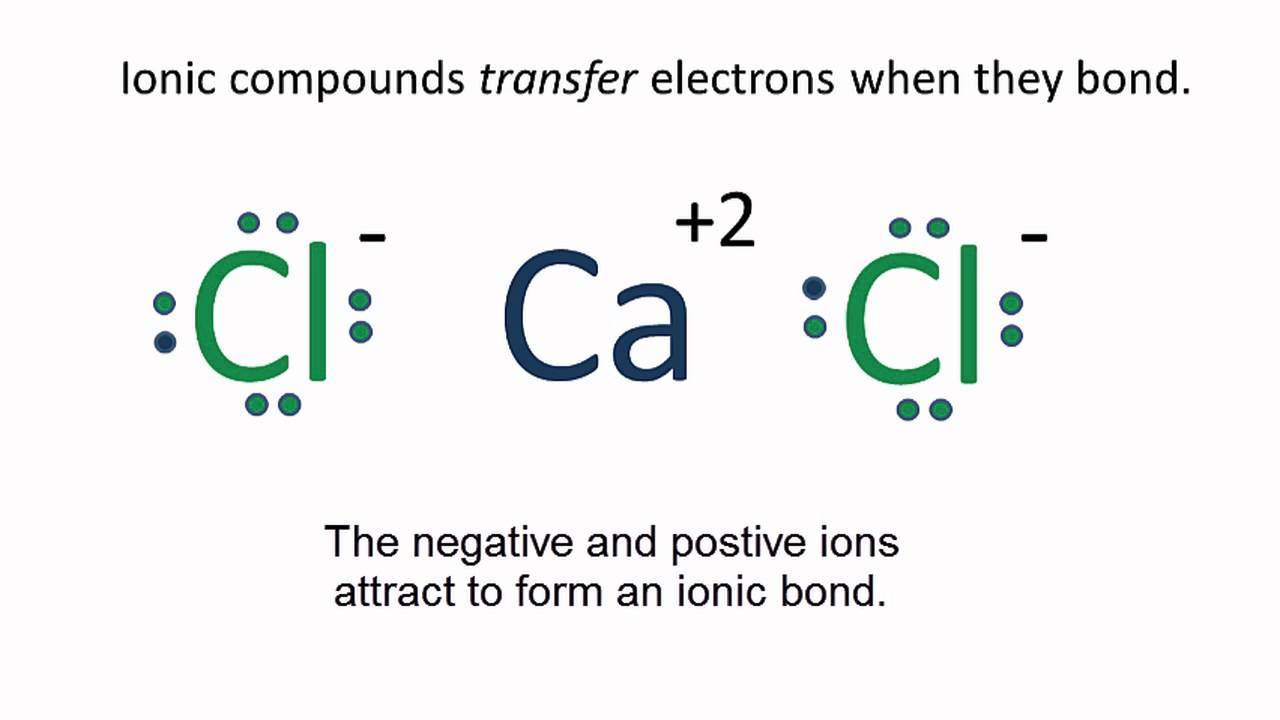
| Search 100+ Lewis Structures on our site. (Opens new window.) |

Lewis Dot Structure Generator
Click the Chemical Formula to see the Lewis Structure
| Steps for Writing Lewis Structures
Advanced Steps Notable Exceptions to the Octet Rule
|